Gauss's Law
Gauss's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Area Vector, Gauss Theorem in Electrostatics, Electric Field due to a Charged Sphere Using Gauss's Law & Electric Flux through a Closed Surface in Uniform Electric Field etc.
Important Questions on Gauss's Law
Assertion: Gauss's law can't be used to calculate electric field near an electric dipole.
Reason: Electric dipole don't have symmetrical charge distribution.
Gauss law is applicable only when there is a symmetric distribution of charge.
A sphere of radius have volume charge density given as
for
for
If electric field at distance from centre is Then will be.
The total flux through the faces of the cube with side of length if a charge is placed at corner of the cube is
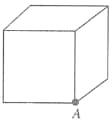
A point charge of is at the centre of cubical Gaussian surface on edge. What is the net electric flux through the surface?
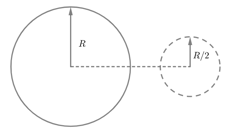
A ring of radius having a linear charge density moves towards a solid imaginary sphere of radius so that the centre of ring passes through the centre of the sphere. The axis of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres of the ring and the sphere. The maximum flux through the sphere in this process is
Flux coming out from a unit positive charge enclosed in air is
A Gaussian sphere encloses an electric dipole within it. The total flux across the sphere is
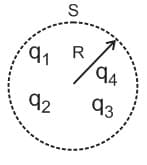
and are point charges located at points, as shown in the figure, and is a spherical Gaussian surface of radius . Which of the following is true, according to the Gauss' law?
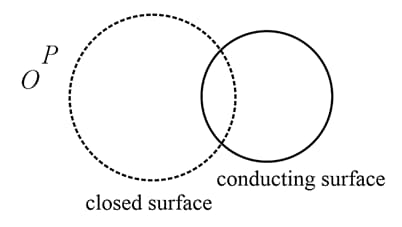
The figure shows a closed surface which intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at the point , the flux of the electric field through the closed surface,
A Gaussian sphere encloses an electric dipole within it. The total flux through the sphere is
Flux coming out from a unit positive charge enclosed in air is
The potential due to an electrostatic charge distribution is where is positive. The net charge within a sphere centred at the origin and of radius is
The electric field intensity outside the charged conducting sphere of radius , placed in a medium of permittivity at a distance from the centre of the sphere in terms of surface charge density is
A metal sphere of radius is charged with . Find the electric intensity at a distance of from the centre of the metal sphere.
A sphere of radius have volume charge density given as
for
for
If electric field at distance from centre is Then will be.
An uncharged thick spherical conducting shell is surrounding a charge at the centre of the shell. Then charge is placed on a point outside the shell. When static equilibrium is reached, the total charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell are respectively
The charge density inside a nucleus is given by where radius of nucleus and The electric field is maximum at If , find the value of .
Two conducting spheres of radii and have equal surface charge densities. The ratio of their charges is ___.
The radii of two conducting spheres are and . When these are given same surface charge density the ratio of electric field intensities at their surfaces is
